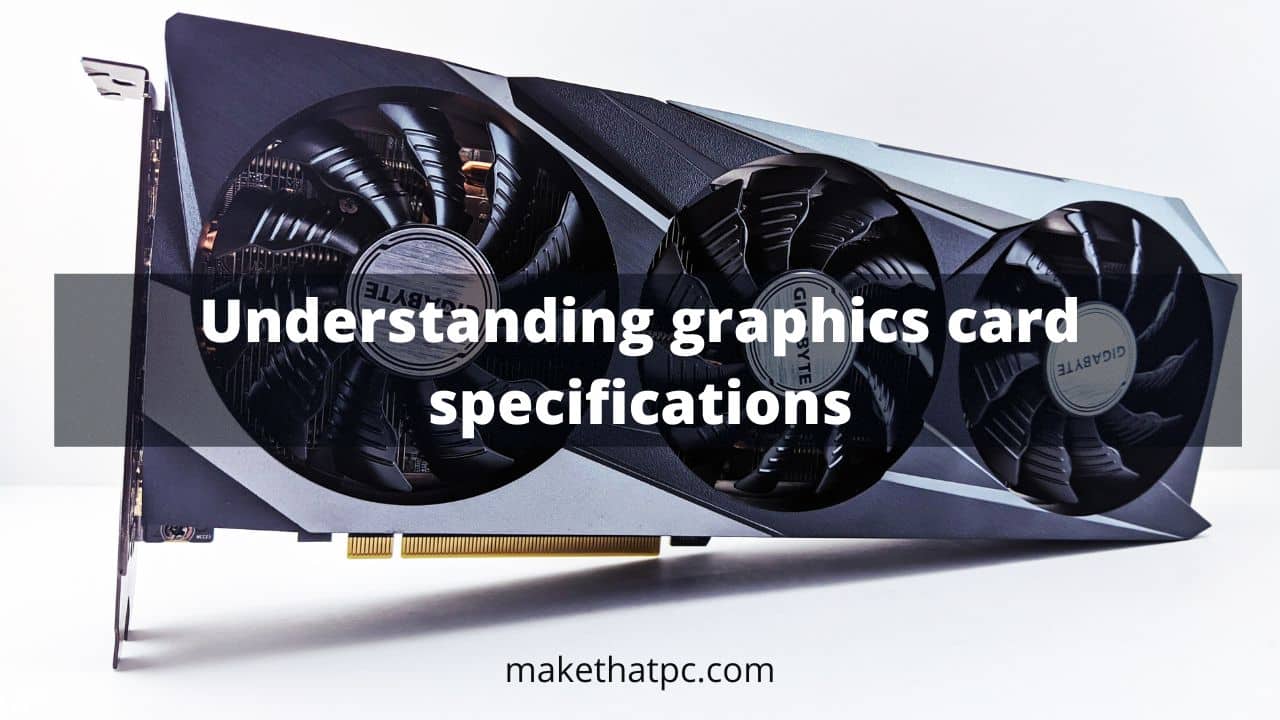
Graphics cards, also known as graphics processing units (GPUs), are a crucial component of any computer system. They are responsible for rendering and displaying images on the screen, and play a vital role in the performance and capabilities of a computer.
Understanding the technical specifications of graphics cards, such as clock speed, memory size and type, and shader units, is essential in order to make informed decisions and get the most out of your computer. Each of these specifications can impact the performance and capabilities of the GPU in different ways, and by considering them, you can choose the right graphics card for your needs and optimize its performance.
What you need to know about the graphics card specifications?
There are many different technical specifications that are used to describe graphics cards, and each of these specifications can impact the performance and capabilities of the card in different ways.
Clock speed, for example, refers to the speed at which the GPU’s processor operates, and is typically measured in megahertz (MHz) or gigahertz (GHz). A higher clock speed generally means that the GPU can process more data and instructions per second, resulting in faster rendering and smoother performance. However, clock speed is just one of several important specifications to consider when choosing a graphics card.
Memory size and type are also important considerations. Graphics cards typically have their own dedicated memory, which is used to store the data and instructions needed to render images on the screen. The size of this memory, typically measured in gigabytes (GB), can affect the performance of the card, as a larger memory size can allow the GPU to store more data and instructions at once, resulting in faster rendering and fewer delays.
In addition, the type of memory used can also impact the performance of the card. Different types of memory, such as DDR3 and DDR4, have different speeds and capabilities, and choosing the right type of memory can make a difference in the performance of the GPU.
Another important specification to consider is the number of shader units, which are essentially small processing units that are responsible for executing tasks related to rendering images. The more shader units a GPU has, the more tasks it can perform simultaneously, which can lead to faster rendering and better performance. However, it is important to note that the number of shader units is not the only factor that affects the performance of a graphics card. Other specifications, such as bandwidth (the rate at which data can be transferred to and from the GPU), power consumption, and cooling capabilities, can also play a role in the performance and functionality of the card.
First Specification: Clock Speed
Clock speed, also known as clock rate, is a measure of the speed at which a graphics card’s processor operates. It is typically measured in megahertz (MHz) or gigahertz (GHz). For example, a graphics card with a clock speed of 1,000 MHz (1 GHz) can process 1 billion instructions per second, while a card with a clock speed of 2,000 MHz (2 GHz) can process 2 billion instructions per second.
For example, consider two graphics cards with the same number of shader units and the same amount of memory, but different clock speeds. The card with the higher clock speed will likely be able to process tasks faster and more efficiently than the card with the lower clock speed.
Second Specification: Memory Size and Type
The size of this memory, typically measured in gigabytes (GB), can affect the performance of the card, as a larger memory size can allow the GPU to store more data and instructions at once, resulting in faster rendering and fewer delays.
Generally, you can easily find out how much VRAM a specific game demands in order to work properly. The better the game’s graphics, the higher will be the demand for VRAM size.
In addition to the size of the memory, the type of memory used can also impact the performance of the graphics card. Different types of memory, such as DDR3 (Double Data Rate 3) and DDR4 (Double Data Rate 4), DDR5, and DDR5, have different speeds and capabilities, and choosing the right type of memory can make a difference in the performance of the GPU. For example, DDR4 memory is generally faster and more efficient than DDR3 memory and may be a better choice for a high-performance graphics card.
These days, it is hard to see graphics cards with DDR3 and DDR4 memory. Now, the latest cards are equipped with very fast DDR6 memory.
Third Specification: Shader Units
Shader units, also known as stream processors, are small processing units that are responsible for executing tasks related to rendering images on the screen. The more shader units a graphics card has, the more tasks it can perform simultaneously, which can lead to faster rendering and better performance.
For example, consider two graphics cards with the same clock speed and the same amount of memory, but different numbers of shader units. The card with more shader units will likely be able to process tasks faster and more efficiently than the card with fewer shader units, as it can perform more tasks simultaneously.
Fourth Specifications: Bandwidth
Bandwidth refers to the rate at which data can be transferred to and from the GPU. A graphics card with a higher bandwidth will generally be able to transfer data faster and more efficiently, resulting in better performance.
Fifth Specification: Power Consumption
The power consumption of a graphics card can be an important consideration, especially for users who are concerned about energy efficiency or who are using a system with limited power capabilities. A graphics card with a lower power consumption may be a better choice for these users.
Conclusion
In conclusion, graphics cards are a crucial component of any computer system, and understanding the technical specifications of these cards is essential in order to make informed decisions and get the most out of your computer.
From clock speed and memory size to shader units and other important specifications, each of these factors can impact the performance and capabilities of the GPU in different ways. By considering these specifications and understanding their significance, you can choose the right graphics card for your needs and optimize its performance to get the best possible performance and capabilities from your computer.

I am Anshul Rana, an experienced author specializing in PC gear reviews and Windows 10 software tutorials. With a strong passion for technology and an in-depth understanding of the PC industry, I provide insightful and detailed analyses of computer peripherals, gaming gear, and software solutions. My writing style is concise yet informative, making complex topics accessible to both beginners and advanced users. Through my reviews and tutorials, I aim to offer valuable guidance, helping readers make informed decisions to enhance their PC experience and explore the vast possibilities of Windows 10 software.